How is blockchain different from traditional database models accenture
How Is Blockchain Different From Traditional Database Models?
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way data is stored and accessed across industries. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized database model that enables secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. In this article, we’ll explore how blockchain differs from traditional database models and why it’s becoming increasingly popular among businesses and individuals alike.
Understanding Traditional Database Models
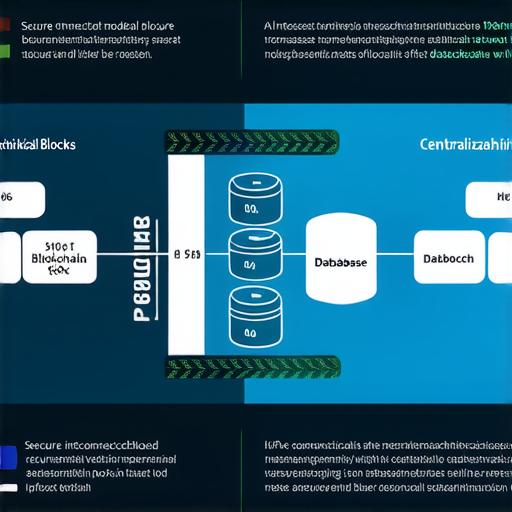
Traditional database models are centralized systems where data is stored in a single location or server. These systems rely on intermediaries, such as banks or other financial institutions, to manage transactions and maintain the integrity of the data. While traditional databases are highly efficient for storing and managing large amounts of data, they have several limitations.
-
Centralization: Traditional database models are highly centralized, which means that all the data is stored in a single location. This can make them vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, and other security threats.
-
Single Point of Failure: Since traditional databases rely on intermediaries to manage transactions, they represent a single point of failure. If an intermediary goes down, the entire system is affected, and transactions cannot be processed.
-
Limited Transparency: Traditional database models are not transparent, which means that users have limited access to the data stored in the system. This can make it difficult to verify transactions and ensure that they are legitimate.
Introducing Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized database model that enables secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. Unlike traditional databases, blockchain is highly distributed, meaning that data is stored across multiple nodes or computers in a network. This provides several advantages:
-
Decentralization: Blockchain technology is decentralized, which means that there is no single point of failure. Even if one node goes down, the system can continue to operate without interruption.
-
Transparency: Blockchain technology is transparent, which means that users have access to all the data stored in the system. This enables greater trust and accountability, as users can verify transactions and ensure that they are legitimate.
-
Security: Blockchain technology is highly secure, thanks to its use of cryptography and consensus algorithms. Transactions on a blockchain are verified by a network of nodes, which makes it virtually impossible for hackers to compromise the system.
Real-life Examples of Blockchain in Action
Blockchain technology is already being used across various industries to enable secure and transparent transactions. Here are a few real-life examples:
-
Cryptocurrencies: Perhaps the most well-known example of blockchain technology is cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. These digital currencies use blockchain to enable secure and decentralized transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
-
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain technology is also being used in supply chain management to improve transparency and traceability of goods. By storing data on a blockchain, companies can track products from production to delivery, ensuring that they are authentic and not counterfeit.
-
Healthcare: In healthcare, blockchain technology is being used to store patient data securely and transparently. By using blockchain, healthcare providers can ensure that patient data is only accessible by authorized personnel, reducing the risk of data breaches and medical errors.
FAQs
Q: What are the main differences between traditional database models and blockchain technology?
A: Traditional database models are centralized systems where data is stored in a single location or server. They rely on intermediaries to manage transactions and maintain the integrity of the data. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, is a decentralized database model that enables secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Q: What are the advantages of using blockchain technology?
A: Blockchain technology provides several advantages over traditional database models. It is highly distributed, providing greater security and resilience. It is also transparent, enabling users to verify transactions and ensure that they are legitimate. Finally, it is secure, thanks to its use of cryptography and consensus algorithms.
Q: What are some real-life examples of blockchain in action?
A: Blockchain technology is already being used across various industries to enable secure and transparent transactions. Real-life examples include cryptocurrencies, supply chain management, and healthcare.



